What is a digital twin?
A digital twin is a virtual representation of a physical object or system that uses real-time data to simulate its behavior. It’s like having an exact digital copy of something in the real world, that you can interact with and experiment on without affecting the original.

Here are some key things to know about digital twins:
- They can be used for a wide variety of purposes, such as:
- Predicting future performance: By analyzing data from sensors attached to the physical object, a digital twin can be used to predict how it will perform in the future. This can be helpful for identifying potential problems before they occur and taking steps to prevent them.
- Optimizing performance: Digital twins can be used to simulate different scenarios and see how the physical object would react. This can be used to find ways to improve the performance of the object, such as by reducing energy consumption or increasing efficiency.
- Training operators: Digital twins can be used to create realistic training simulations for operators of physical objects. This can help to improve the safety and efficiency of operations.
- They are still a relatively new technology, but they have the potential to revolutionize many industries. For example, digital twins are being used in the following industries:
- Manufacturing: To predict when equipment will need to be repaired or replaced.
- Healthcare: To monitor patients’ health and predict potential complications.
- Aerospace: To design and test new aircraft.
- Energy: To optimize the performance of power grids.
Overall, digital twins are a powerful tool that can be used to improve the way we design, operate, and maintain physical objects. As the technology continues to develop, we can expect to see even more innovative applications for digital twins in the years to come.
Different types of digital twins.
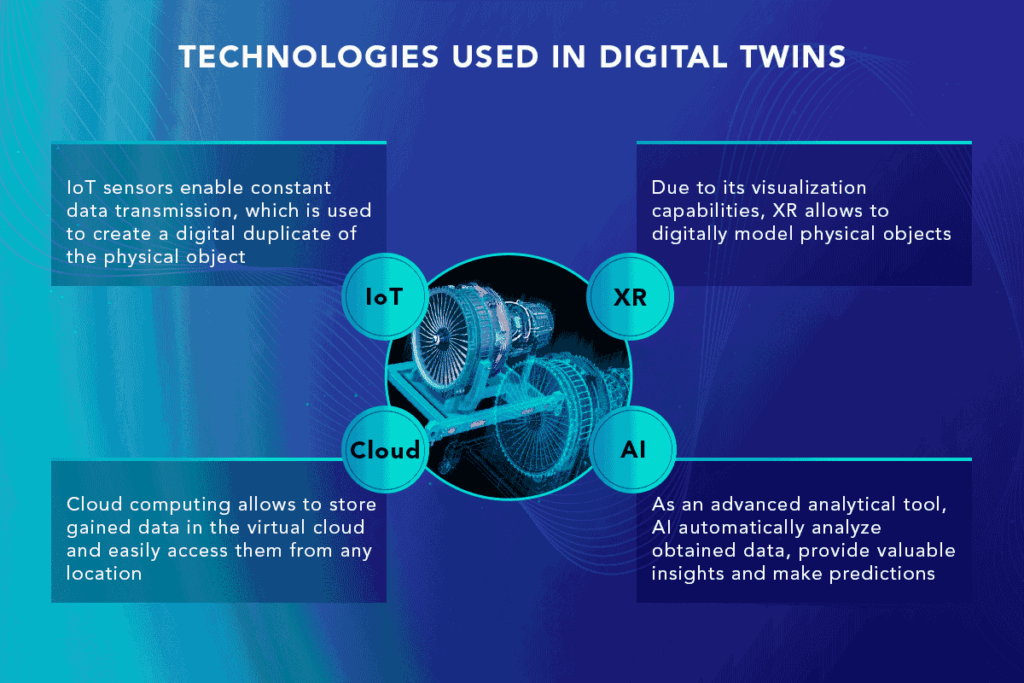
Sure, there are four main types of digital twins, each focusing on a different level of complexity:
1. Component Twins:
- The most basic level, representing individual components like a sensor, valve, or pump.
- Used to monitor the health and performance of individual components.
- Can help identify potential problems early on and prevent downtime.
3. System Twins:
- Represents a complex system made up of multiple assets, such as a manufacturing plant or power grid.
- Simulates the interactions between different assets in the system.
- Used to optimize the overall performance of the system and identify potential bottlenecks.
4. Process Twins:
- Represents a business process, such as supply chain management or customer service.
- Models the steps involved in the process and identifies areas for improvement.
- Used to automate tasks, optimize workflows, and improve the customer experience.
- The type of digital twin used will depend on the specific application. For example, a component twin might be used to monitor a sensor in a jet engine, while a system twin might be used to optimize the performance of a power grid.
The features of digital twin-
Sure, here are some key features of a digital twin:
1. Connectivity:
- A digital twin is linked to its physical counterpart through sensors and other data collection devices.
- This real-time data flow allows the digital twin to constantly update and reflect the state of the physical object.
2.Data Analytics:
- The data collected from the physical object is fed into the digital twin for analysis.
- This analysis can be used to identify patterns, predict future behavior, and optimize performance.
3. Real-time Updates:
- Digital twins are constantly updated with new data from their physical counterparts.
- This allows them to provide an accurate and up-to-date picture of the physical object’s state.
4. Simulation:
- Digital twins can be used to simulate different scenarios and see how the physical object would react.
- This can be helpful for identifying potential problems, testing new designs, and training operators.
5. Interactivity:
- Some digital twins can be interacted with in real-time.
- This allows users to control the physical object through the digital twin, or to experiment with different settings and configurations.
6. Scalability:
- Digital twins can be scaled to represent anything from a single component to a complex system of systems.
- This makes them adaptable to a wide range of applications.
7. Flexibility:
- Digital twins can be customized to meet the specific needs of different applications.
- This allows them to be used in a variety of industries and for a variety of purposes.
I hope this provides a comprehensive overview of the features of digital twins!